A is a method of recording employee attendance using biometric identifiers, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans. The system works by capturing a unique biological feature of an individual, verifying their identity, and logging their attendance in real-time.
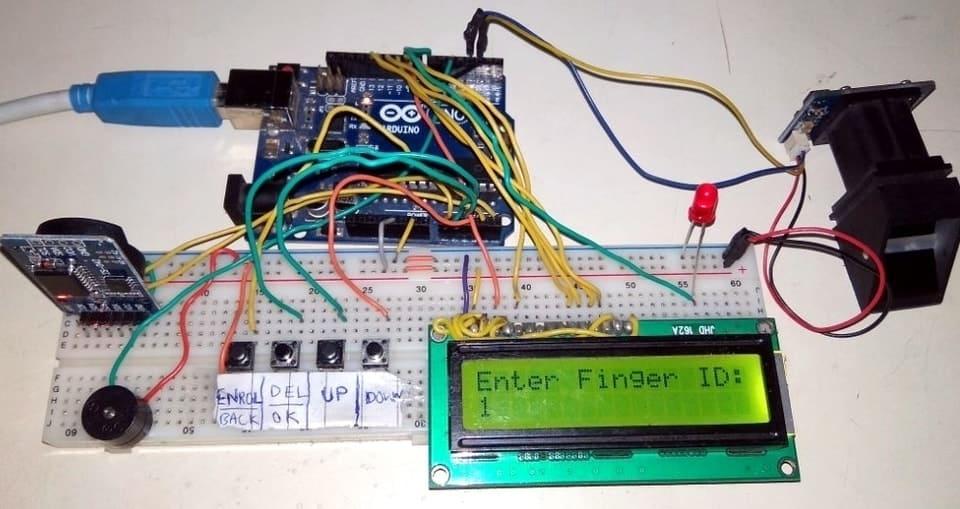
Components of a Biometric Attendance System:
- Biometric Scanner: A device that captures biometric data such as a fingerprint scanner, facial recognition camera, or iris scanner.
- Software: The system that processes and stores attendance data, manages employee records, and generates reports.
- Database: Stores the biometric templates (fingerprints, facial recognition data) and attendance logs.
- User Interface: Allows employees to check in and out, view their attendance status, and interact with the system.
- Networking: For centralized systems, it enables data synchronization across multiple locations or devices.
How it Works:
- Enrollment: An employee's biometric data (e.g., fingerprints or facial features) is captured and stored in the system during the enrollment process.
- Authentication: When the employee arrives for work, they present their biometric data (e.g., fingerprint or face) to the scanner.
- Verification: The system compares the newly captured data with the stored data to verify the employee's identity.
- Logging: Once verified, the system logs the employee's attendance, including the time of entry or exit.
- Data Management: The system generates reports for HR or managers, showing attendance records, late arrivals, and absences.
Advantages:
- Accuracy: Biometrics are unique to each individual, reducing the risk of fraud or buddy punching (where one employee clocks in for another).
- Convenience: Employees don’t need to remember PINs or swipe cards; just a quick scan of their fingerprint or face is enough.
- Cost-Effective: Saves on the need for physical cards or manual recording.
- Security: Prevents unauthorized access and ensures only registered employees can log attendance.
- Automation: Eliminates manual data entry, reducing errors and administrative workload.
Disadvantages:
- Privacy Concerns: Storing biometric data raises concerns about security and privacy. It's crucial to ensure proper data encryption and protection.
- Initial Setup Cost: Biometric devices and software can be expensive initially.
- Technical Issues: Scanners may sometimes malfunction or not work as expected (e.g., dirty fingerprints, lighting issues for facial recognition).
- False Positives/Negatives: In some cases, there may be issues with correctly identifying employees, especially if the system is not calibrated correctly.
Common Types of Biometric Systems:
- Fingerprint-based: Uses a fingerprint scanner to authenticate employees.
- Facial Recognition: Uses cameras to recognize and authenticate employees based on their facial features.
- Iris Recognition: Uses the unique patterns in an individual’s iris for identification.
- Voice Recognition: Verifies identity based on the employee’s voice pattern.
- Hand Geometry Recognition: Analyzes the shape and size of the employee's hand.
Use Cases:
- Corporate Offices: Used for tracking employee attendance, especially in large organizations.
- Schools: For monitoring student attendance in an automated manner.
- Factories: To ensure accurate and timely worker attendance.
- Government Offices: For security and attendance tracking in government agencies.
.jpeg)
